Economy
Economy
The economy operates as a complex system that evolves over time, influenced by various factors such as government policies, market demand, and global trade. Long-term economic growth is one of the key strategies for ensuring financial stability and prosperity. Economists and policymakers analyze market trends, inflation rates, and investment flows to predict and shape economic development, aiming to create sustainable growth and improved living standards for individuals and businesses.
About Economy
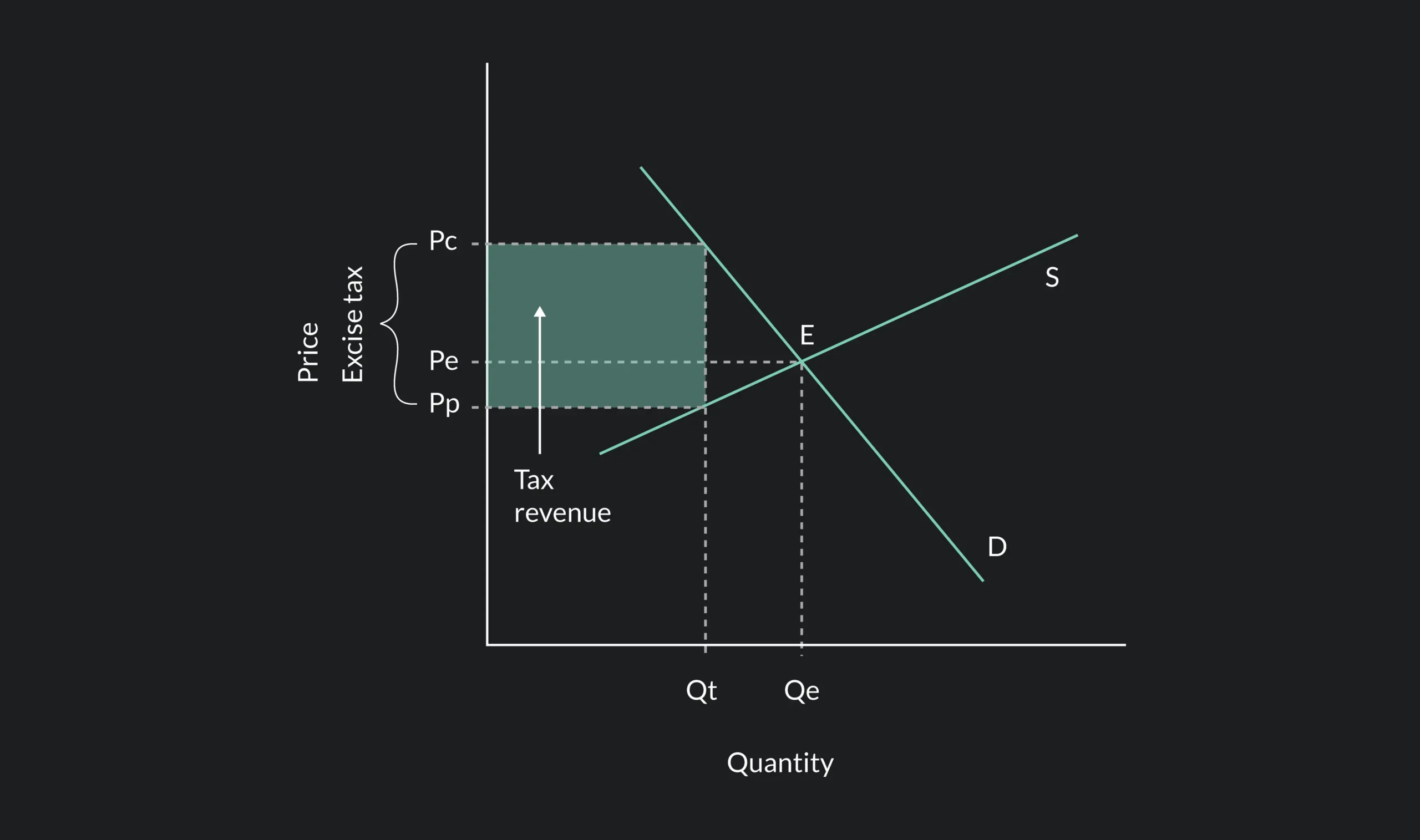
When we think of market structures, monopolies are often seen as controversial yet fascinating entities. Unlike competitive markets where numerous firms compete, a monopolist controls the supply and...
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the economy, and how does it work?▼
The economy refers to the system by which goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed. It operates through the interaction of businesses, consumers, and governments, where supply and demand influence prices, employment levels, and overall economic growth. Key components include industries, labor markets, trade, and financial institutions.
What are the main factors that affect economic growth?▼
Several factors influence economic growth, including:
- Consumer spending – The demand for goods and services drives production and job creation.
- Government policies – Taxes, interest rates, and public spending impact economic stability.
- Investment and innovation – Technological advancements and capital investments improve productivity.
- Global trade – Import and export activities affect national economies and exchange rates.
- Natural resources – Availability of raw materials and energy sources can impact economic expansion.
What is inflation, and why does it matter?▼
Inflation is the rate at which the prices of goods and services rise over time, reducing purchasing power. Moderate inflation is normal and indicates a growing economy, but high inflation can decrease the value of money, making everyday expenses more costly. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, use monetary policies to regulate inflation by adjusting interest rates and controlling money supply.
What is the difference between a recession and an economic boom?▼
A recession is a period of economic decline, marked by reduced consumer spending, rising unemployment, and lower business investments. It often occurs when GDP contracts for two consecutive quarters.
An economic boom, on the other hand, is a period of strong growth, where businesses expand, employment rises, and consumer confidence increases, leading to higher spending and investment.
How do interest rates impact the economy?▼
Interest rates, set by central banks, influence borrowing and spending habits.
- Low interest rates encourage borrowing and investment, stimulating economic growth.
- High interest rates slow down inflation by making loans more expensive, reducing consumer spending and business expansion.