Bahking
Banking
Banking is an essential component of the financial system, providing individuals and businesses with secure ways to manage their money. Unlike short-term financial transactions, banking services focus on long-term financial stability, offering savings, loans, and investment opportunities. Banks play a crucial role in the economy by safeguarding deposits, facilitating transactions, and providing credit to support economic growth. Through various financial products, they help customers build wealth and achieve financial security over time.
About Banking
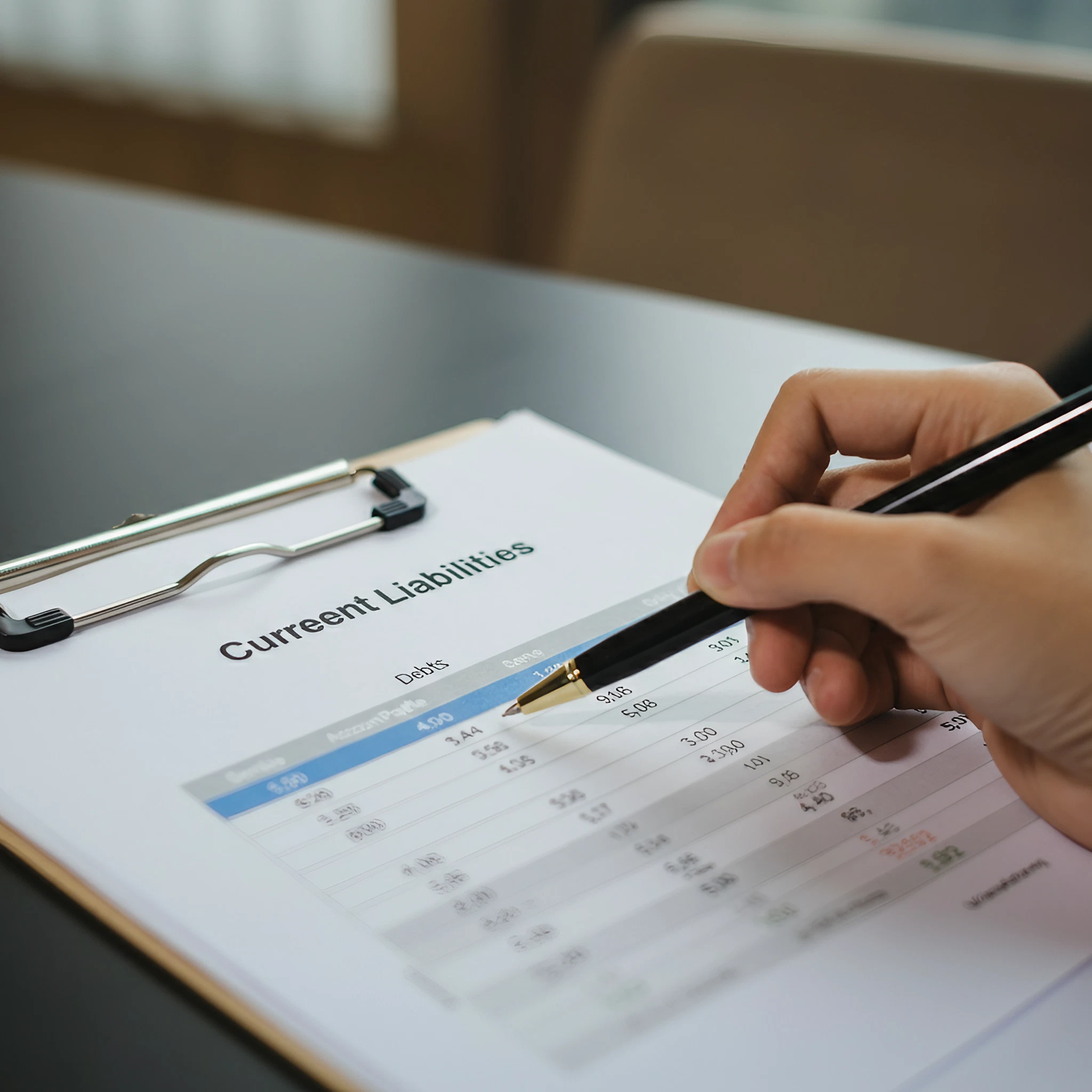
When managing a company’s finances, understanding the concept of current liabilities is vital for maintaining financial health, planning cash flow, and demonstrating solvency to investors or creditors. One...
Frequently Asked Questions
How does banking work?▼
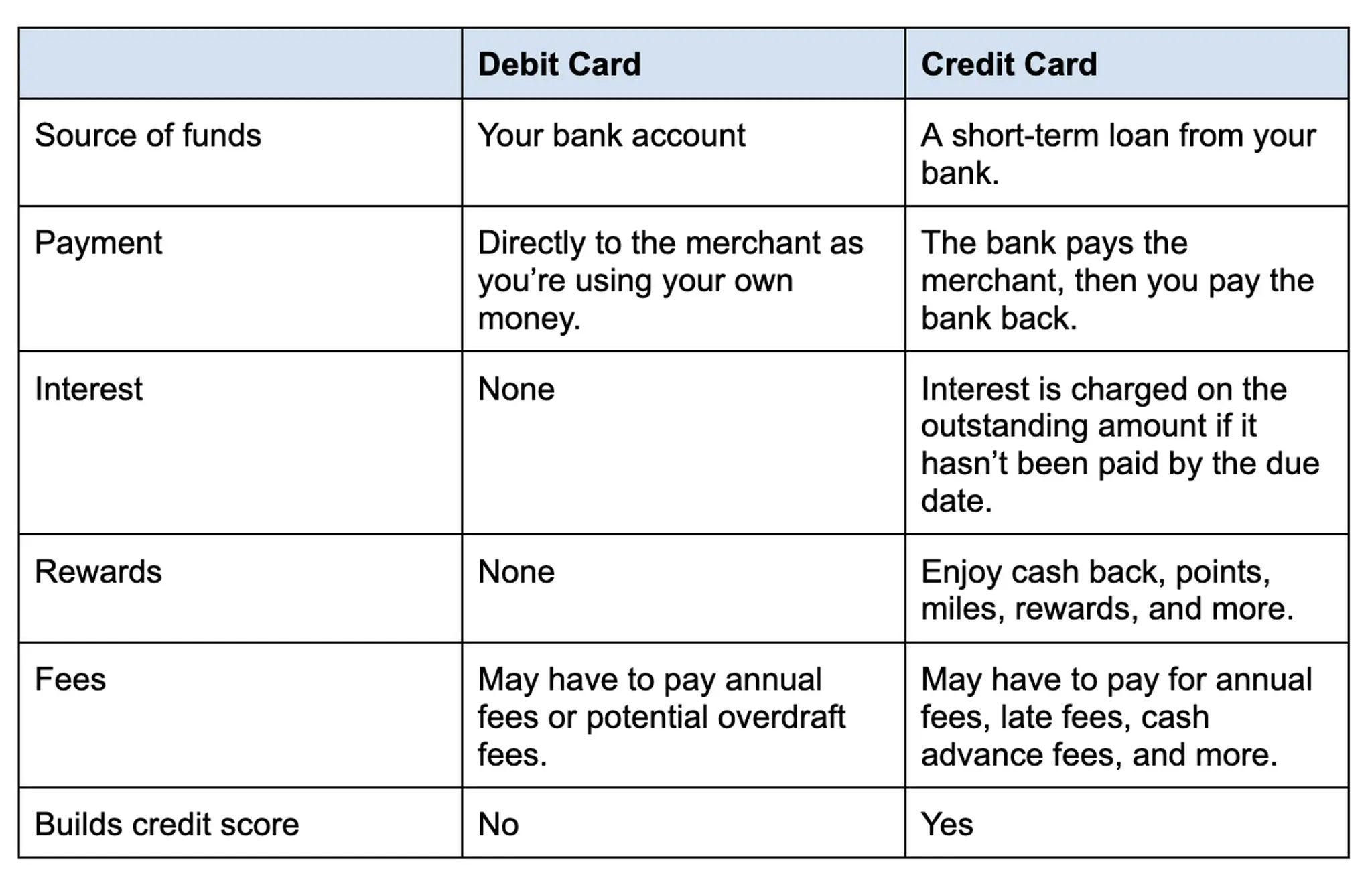
Financial institutions play a crucial role in the economic system by offering essential services to individuals and businesses alike. They ensure the safekeeping of funds while granting secure access to deposits. Customers can efficiently manage their finances through checking accounts, ATMs, and electronic transfers. Additionally, banks enable depositors to earn interest on their savings through various accounts, including savings accounts, certificates of deposit, and specific demand deposit accounts.
What is the history of deposit insurance? ▼
In response to the widespread bank failures during the Great Depression, the federal government established the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) in March 1933 to insure bank deposits. This independent agency was designed to restore public trust in the financial system by protecting customer funds. Today, the FDIC provides insurance coverage of up to $250,000 per depositor, per account, ensuring greater stability and confidence in the banking sector.
Are big banks a safer option for deposits?▼
Major financial institutions tend to offer greater stability compared to smaller banks, such as state and community banks, as well as other financial entities. While the U.S. banking system remains robust across all levels, larger banks, often operating under national charters, are required to provide FDIC insurance for deposits. Their adherence to federally mandated capital reserve requirements further reduces the risk of default, ensuring a higher level of financial security for depositors.
What is a national bank? ▼
A national bank is a federally chartered commercial bank regulated by the U.S. Comptroller of the Currency. As a member of the Federal Reserve System, it also holds an investing stake in its respective district Federal Reserve Bank. Additionally, national banks are mandated to be part of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), ensuring that customer deposits are protected under FDIC insurance coverage.
What are bank fees? ▼
Bank fees refer to charges imposed by financial institutions on both personal and business customers for various banking services, such as account setup, maintenance, and transactions. Common examples include wire transfer fees, ATM withdrawal fees, non-sufficient funds (NSF) fees, and late payment penalties. These fees help cover operational costs and vary based on the bank and type of account.